Internal capsule cerebrum.
Openings in roof of fourth ventricle.
The cavity or fossa of the.
It is widest at the level of the pontomedullary junction.
The lower has a median aperture foramen of magendie.
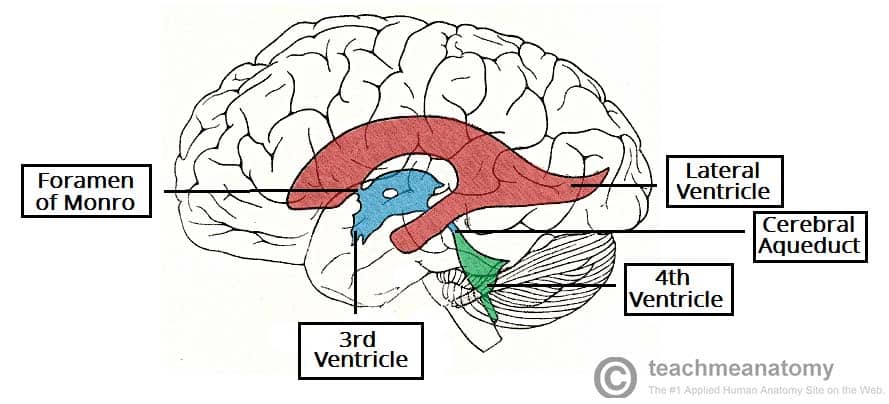
The two lateral ventricles the third ventricle and the fourth ventricle.
The sidewalls are formed by the veli and cerebellar peduncles.
An opening in the roof of the fourth ventricle that connects to the subarachnoid space lateral apertures two openings in the side walls of the fourth ventricle that connect to the subarachnoid space.
The fourth ventricle contains choroid plexus along its roof along the tela choroidea which may protrude out the lateral foramina of luschka.
It corresponds to the ventral surface of the cerebellum.
The understanding of the 4th ventricle is important firstly because it s strategically set in the middle of critical structures existing in the medulla pons and cerebellum and second because its roof possesses 3 essential openings which allow the csf to escape from the ventricular system of the brain to the subarachnoid space.
There are four in all.
The roof of the fourth ventricle has presents a tent like apex at the intersection of it s superior and inferior.
The lateral walls of the fourth ventricle are formed by the cerebellar peduncles.
The upper portion of the roof is formed by the cerebellum.
To the rights is a drawing of the ventricles.
View chapter purchase book.
The floor of the fourth ventricle the rhomboid fossa see fig.
The only naturally occurring openings between the ventricles of the brain and the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain are the foramina of luschka and magendie in the fourth ventricle.
The fourth ventricle has a roof at its upper posterior surface and a floor at its lower anterior surface and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior side of the ventricle to the structures on the anterior side.
This leads to excessive accumulation in the ventricular system thereby producing internal hydrocephalus.
10 3 is formed by the pons and medulla fig.
Fourth ventricle lateral walls.
The roof of ventricle is diamond shaped and can be divided into superior and inferior parts.
The obex is the most caudal tip of the fourth ventricle.
The roof of fourth ventricle is the dorsal surface of the fourth ventricle.
Cerebrospinal fluid escapes through this opening and lateral apertures into the subarachnoid space.
As you look at the drawing imagine the ventricles as chambers filled with fluid.
The superior part of.
If the opening of fourth ventricle foramen of magendie and luschka are blocked by tumor or adhesions of arachnoid mater the csf cannot enter the subarachnoid space from the ventricular cavity.